What is RemoteWebDriver?
RemoteWebDriver in Selenium Webdriver implements each of the JSONWireProtocol commands and maps them into an action that can be performed on a remote machine.
RemoteWebDriver is a Class in the
package org.openqa.selenium.remote inside the Client Project of WebDiver. RemoteWebDriver.class implements multiple interface like WebDriver(Yes WebDriver is an Interface not a Class as I have seen many people confused about this information), FindsById, FindsByClassName, FindsByLinkText etc.package org.openqa.selenium.remote;
public class RemoteWebDriver implements WebDriver, JavascriptExecutor,
FindsById, FindsByClassName, FindsByLinkText, FindsByName,
FindsByCssSelector, FindsByTagName, FindsByXPath,
HasInputDevices, HasCapabilities, Interactive, TakesScreenshot
JavaDoc for the RemoteWebdriver explains all the details about the Class and its Methods,SubClasses and Interface implement in gitHub Url.
Now the question is who use this RemoteWebdriver.class?
All the Browser Driver Class are the child class of RemoteDriver means they are extending the RemoteWebDriver.Class. Few examples of the drivers are below..
public class ChromeDriver extends RemoteWebDriver
implements LocationContext, WebStorage, HasTouchScreen, NetworkConnection {
public class FirefoxDriver extends RemoteWebDriver {
public class InternetExplorerDriver extends RemoteWebDriver {
So whenever in our test class we create a Driver instance by using the line
WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver(); we are always creating an instance of the RemoteDriver Class automatically.Can we use the RemoteWebDriver class directly in our Test?
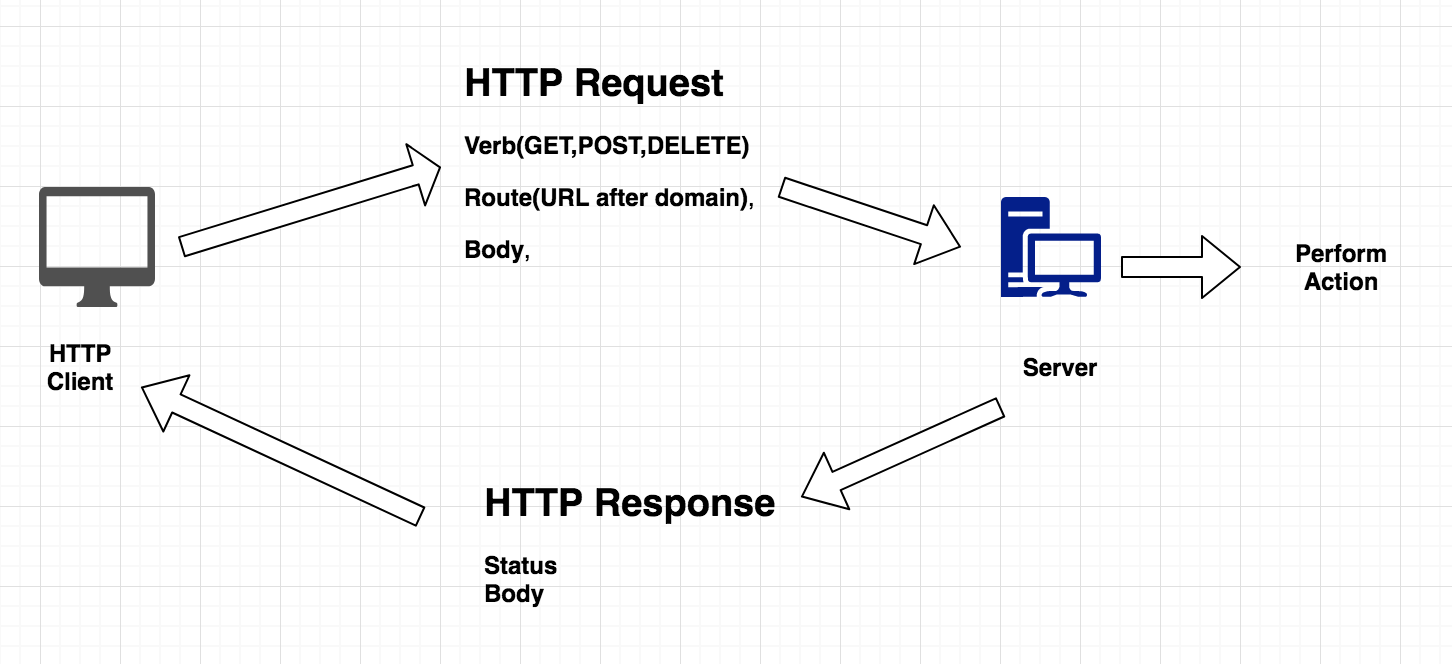
Yes we can directly create an instance of the RemoteWebDriver Class as well because drivers are local implementation that controls a browser running on the local machine, If we want to Run our Test Cases not only in our local browsers but on the distributed systems like cloud application Sauce Lab or BrowserStack or Selenium Grid. We must use RemoteWebDriver class instance and pass the proper DesiredCapabilities like:
public void createChromeDriverForRemote(){
WebDriver driver = new RemoteWebDriver(remoteUrl,
DesiredCapabilities.chrome());
}
How RemoteWebDriver Works?
Let’s understand what are the methods involved and class RemoteWebDriver use to perform any action from our test programme. I am going to use ChromeDriver here for the explanation and will be trying to explain step by step.
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver", "/path/to/chromedriver");
DesiredCapabilities desiredCapabilities = DesiredCapabilities.chrome();
WebDriver driver = new RemoteWebDriver(new URL(url), desiredCapabilities);
driver.get("http://www.google.com");
When we create an instance of the RemoteWebDriver by passing the URL and DesiredCapabilities object using the following line
WebDriver driver = new RemoteWebDriver(new URL(url), desiredCapabilities);
Constructor method of RemoteWebDriver class is invoked and create a session for your test scripts. There are multiple methods call inside and you receive the sessionId for you Test. RemoteWebDriver Class use two another important class:
DriverCommandExecutor.class and HttpCommandExecutor.class
HttpCommandExecutor.class has a very important method as execute which is used to execute all the WebDriver commands and initializing the HttpClient which is used to send and receive the HTTP requests between server and client.
public Response execute(Command command) throws IOException {
...........
}
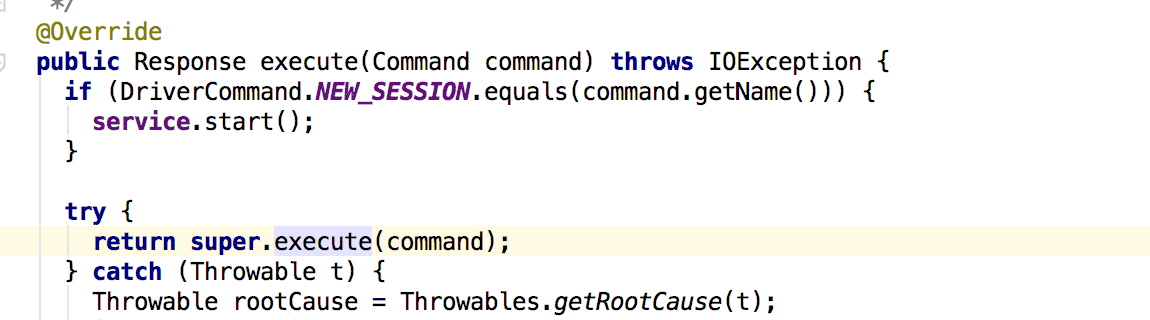
So every command like Get or findElement goes through this execute method and send to the server and return the Response Class object. All the details about the methods and class details are explained in the selenium API javaDocs. I recommend everyone to build webdriver on there local machines and try to look into the classes and methods.